A “flooded battery” is the same as a “wet cell battery.”
Batteries have been utilized for centuries and archeological proof indicates that galvanic cells may have been utilized 2,000 years back. The wet cell battery, also known as “flooded battery,” was one of the first present day battery types to be created for common use. Its history goes back to 1836, when John Frederic Daniell made the first wet cell battery.
Irrespective of the fact that the battery created by John Frederic Daniell was delicate and dangerous to move, it was considered good for the time. Since then, people with the help of their skill and technology upgraded wet cell batteries and today they are available passing all the tests and requirement criteria.
How It Works
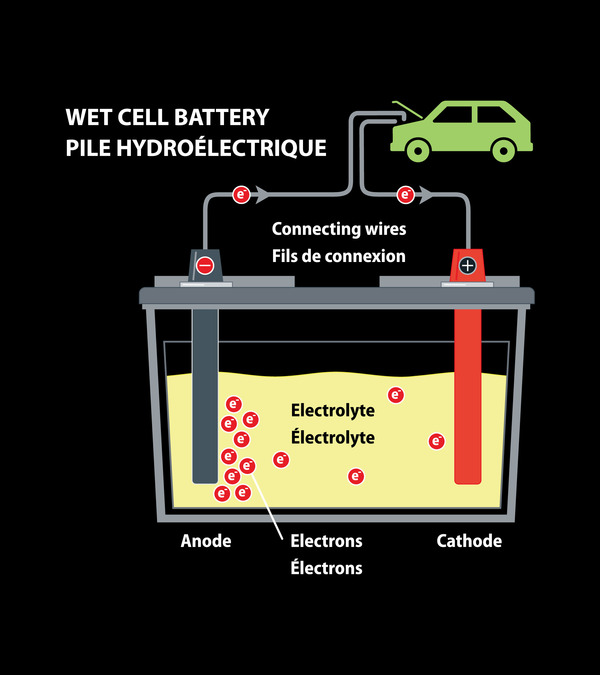
Let’s discuss its working mechanism first. The battery terminals are connected with the load causing a chemical reaction between electrolyte, lead and lead oxide. This chemical reaction causes the flow of electricity to the load via terminals that further lead to the removal of sulfuric acid from the solution that is reinforced to the plates. At the point when the battery is charged by a reverse current, the bonds between the sulfuric acid and plates are broken and the acid comes back to the solution, giving it a chance to provide more power for future use.
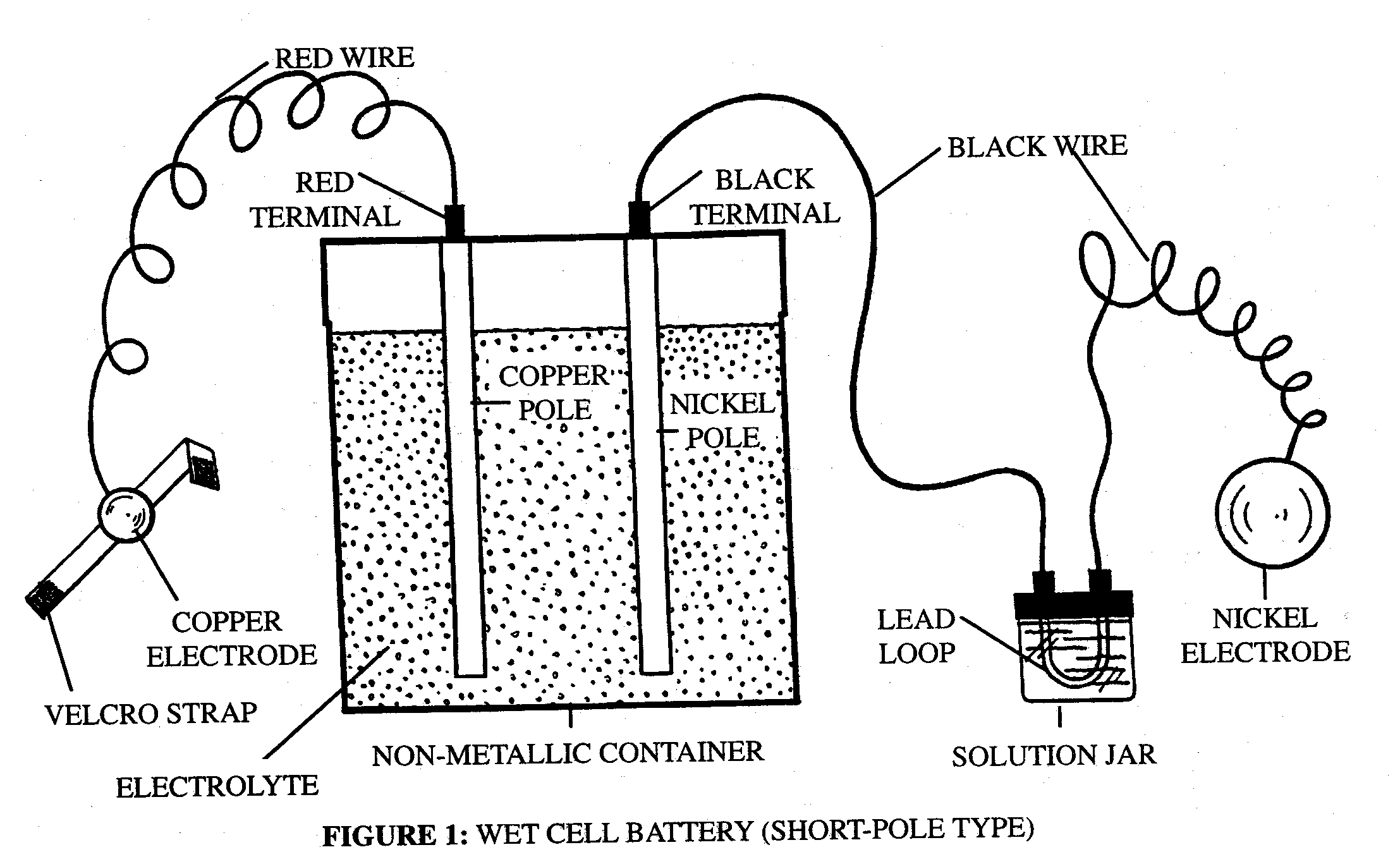
Types of Wet Cell Battery
Wet cells, in the same way as dry cells, fall into two fundamental classifications :
a) Primary (non-rechargeable): As the name suggests, in primary battery type the electricity producing chemical reaction cannot be reversed, so once exhausted it can never be charged again.
b) Secondary (rechargeable): However, in secondary battery types, this chemical reaction can be reversed and thus battery can be charged “n” number of times.
The most common example of wet cell batteries are our very own car batteries.
Use and Replacement
After continuous use over the years, a wet cell battery can no more give sufficient power to the load connected to it. This happens because with use, the plate material erodes, thereby causing reduction in their size. The eroded material from the plates of the battery settles down leaving even smaller plates and killing out the battery power completely.
A wet cell battery dies quicker under hot conditions, since the heat makes the plates either gain or lose material and reduces the water from the electrolyte solution. Also, excessive vibration, prolonged use of the battery and overcharging can result in quicker loss of battery.
Health and Safety Precautions
Most wet-cell batteries available today are sealed so nobody making use of battery is exposed to the very dangerous lead and sulfuric acid. Then again, when in active form, the electrolyte solution present in the battery produces gasses which are highly combustible. Thus, as a general rule, all the manufacturers use labels that warn the consumers about the dangers that a battery acid and gasses.
Small list of advantages offered by wet cell batteries:
a) Initial costs that are easy on every pocket
b) Water can be manually added when needed
c) Good for high current applications
d) Excellent tolerant of improper recharge voltages
e) Easy replacement
f) Some of the available designs are even good for deep cycle applications
g) Excellent for working at extreme cold weather conditions
Related articles:



