For many car enthusiasts, the term “alternator” would simply mean an electro-mechanical device that charges the SLI battery of their vehicle. It is being driven by the engine through a drive belt connected to the alternator’s shaft. For most vehicle mechanics, the definition would be the same, only that they could further explain that what makes the alternator work are the rotating magnetic fields and the stationary coils of wire. It is always good to ask a mechanic for advice, but since they may not be always around, then it would be also good for you to learn the basics of the alternator.
Inside an Alternator
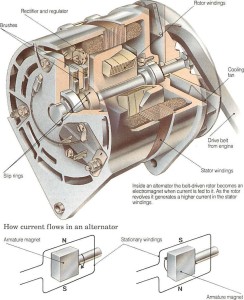
Putting it in layman’s term, alternator is what produces the electricity that charges up your vehicle’s battery, specifically the SLI battery. This electricity is what is known as the alternating current (AC). Inside the alternator there are rotating magnets known as the rotor and the conductor wound in coils on an iron core called the stator. Whenever the stator makes one complete rotation, an electromotive force (EMF) in the form of current is induced in the stator thus producing the AC voltage. Other parts of an alternator are the slip rings, brushes, field coils and permanent magnet.
Image Source: How a Car Works Website
Alternator at Work
The DC voltage (or the rectified AC voltage) is what will charge up your vehicle’s battery. Whenever the battery discharges electricity for your vehicle’s starting, lighting and ignition (also known as the SLI system), it needs to be recharged. The alternator does it all. It converts the engine’s mechanical energy into electrical energy that continuously charges up the battery for an almost infinite number of cycles. It is that only the wear and tear of the alternator and other parts connected to it that will put these cycles to a halt.
Related Articles: