The Lithium-Ion battery is one of the most widely used rechargeable batteries for portable consumer electronics such as laptops and mobile phones. They have high energy densities and no memory effect (effect which causes battery to hold less charge) compared to its contemporaries. Lithium-Ion batteries are also gaining popularity in electric car, military and aerospace applications.
Like all batteries, Lithium-Ion batteries consist of three essential components: the positive electrode, the negative electrode and the electrolyte. In most Lithium-Ion batteries, a positive electrode is a metal oxide, the negative electrode is carbon and the electrolyte is a Lithium salt in an organic solvent.
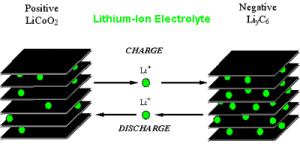
Functioning:
In Lithium-Ion batteries, lithium ions move from the negative electrodes to the positive electrodes through the non-aqueous electrolyte, during discharge. During charging, Lithium ions move from the positive electrode to the negative electrode, where they get inserted in the porous electrode in a process known as Intercalation.
The capacity, energy, cost, performance and safety of Lithium-Ion batteries vary differently on the types of materials used. Lithium cobalt oxide provides high energy densities but comes with a safety risk; they are widely used in portable handy devices such as mobile phones. On the other hand, Lithium iron phosphate and Lithium manganese oxide offer longer lives with low energy devices; they are widely used for electric tools and medical equipments.
Advantages:
1. Li-On batteries are lighter when compared to other batteries of the rechargeable family.
2. They do not have memory effect.
3. Improved safety factors when compared to other rechargeable batteries. They are more resistant to overcharge and less chance of leakage of electrolyte.
4. Do not contain any toxic or hazardous elements.
5. Low self discharge rate, typically stated by manufacturers to be 1.5-2% per month.
Disadvantages:
1. More expensive than Nickel-Cadmium batteries.
2. Internal resistance increases with cycling and age.
3. Fragile and requires a protection circuit to maintain safe operation.
Related posts:
How to wire batteries in parallel?
Understanding Lithium-Air Battery