As the name implies, thin-film rechargeable lithium-ion battery is a secondary cell consisting of intercalated lithium compound as the electrode material and constructed into thinner, lighter and denser layers of solid-state lithium polymers. Such battery is a variant of the conventional lithium-ion polymer battery (a.k.a. Li-poly). What makes it a bit different is that it is made of thinner materials ranging from nanometers to micrometers in total thickness. A packaged thin-film Li-On battery measures only about a few millimeters thick. Li-poly batteries are often available in “pack” and “pouch” packaging and therefore measure up to a few centimeters.
Technology Behind Thin-film Batteries
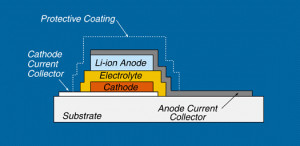
A thin-film Li-On battery is consisting of substrate, electrolyte, current collector, anode, cathode, and a separator. You will notice that, when compared to the conventional lithium-ion batteries, there is the presence of the substrate and current collector.
A substrate is a thin layer of ceramic material that serves as the foundation layer in the deposition process. The current collector is a thin sheet of metal that serves as the conducting path between the electrodes and the external circuitry of the battery. These two new components serve as the initial layers in producing thin-film batteries. This production process is known as thin-film printing technology, an advanced chemical-physical process often used in the manufacturing of optics and semiconductor devices.
Thin-Film Li-On Battery Deposition
Image Source: ORNL Website
Here is how thin-film printing basically works in lithium-ion batteries. It is called “deposition”, the step-by-step process of printing the film layers. The typical order of depositing components in thin-film Li-On batteries is as follows: substrate – cathode current collector – cathode – electrolyte – anode – anode current collector – protective coating. It is, however, important to note that such order can change depending on the printing technology method used.
The current collectors are deposited on top of the substrate and are usually made of silver nanowires and carbon nanotubes (CNT). The deposition of cathode materials can be done in various methods, the most common of which are the Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). The electrolyte materials used in thin-film lithium-ion batteries are solid polymer-based and are deposited over the cathode material through the Magnetron Sputtering process. One advantage of solid-polymer electrolytes is that they can both act as electrolyte and separator.
Scientific Advancements in Thin-Film Batteries
Achieving longer cycle life and better energy density in thin-film batteries has been the focus of many scientists in the recent years. In early 2000, flexible thin-film batteries were introduced to the market. In 2014, the discovery of an energy device for flexible electronics that packs a lot of power triggers innovations in the battery industry. In the next post, we will discuss about Polymer Technology and Nanotechnology, two important scientific breakthroughs that are continuously improving the thin-film batteries.
Related articles:
Energy Device for Flexible Electronics Packs a Lot of Power
What is a Lithium-ion Polymer Battery?